

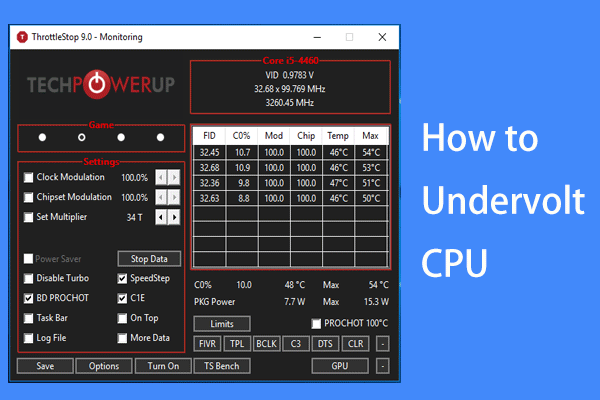
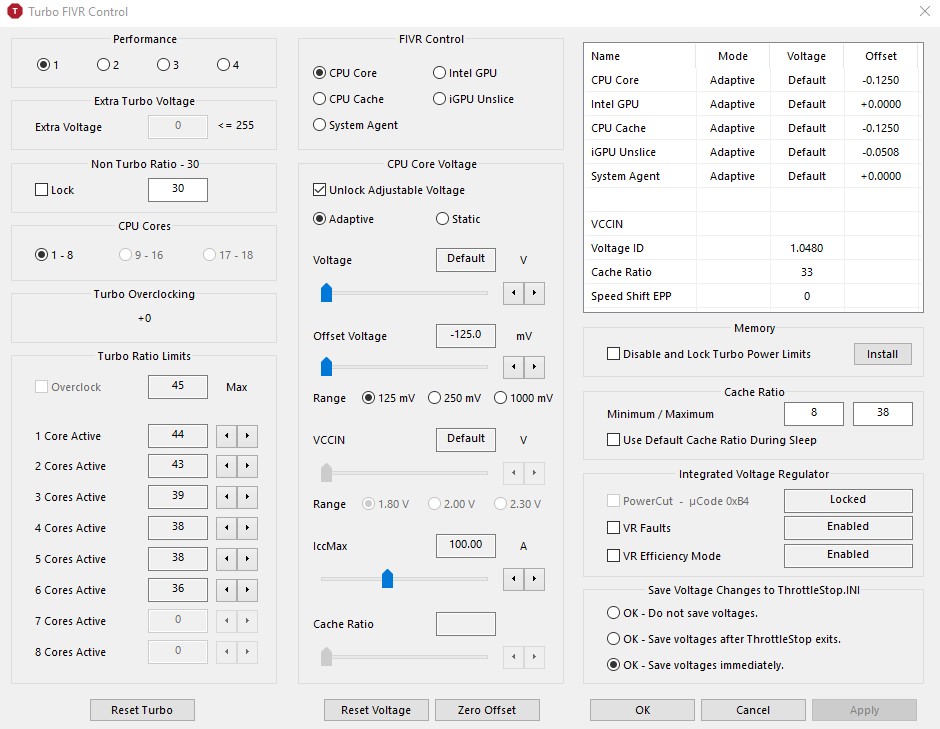

This might also be necessary if stability problems are encountered at higher settings, especially in a PC with several memory modules of different clock speed. Newer and faster RAM may be underclocked to match older systems as an inexpensive way to replace rare or discontinued memory. Underclocking a GPU will reduce performance, but this decrease will probably not be noticeable except in graphically intensive applications. The GPU can then be overclocked for more graphically intense applications, such as games. internet browsing and word processing), thus allowing the card to operate at lower temperature and thus lower, quieter fan speeds. For instance, it is possible to set a GPU to run at lower clock rates when performing everyday tasks (e.g. Underclocking can also be performed on graphics card processor's GPUs, usually with the aim of reducing heat output. Reduced instruction set computer (RISC) models can help makers build devices that work on less power. In addition to providing underclocking features, manufacturers can choose to limit the capability of a machine in order to make it more efficient. Laptop computers and other battery-operated devices often have underclocking settings, so that batteries can last longer without being charged. It can also lower the amount of energy needed to run the device. Underclocking can help with excessive heat buildup, because lower performance will not generate as much heat inside the device. Manufacturers add underclocking options for many reasons. Many computers and other devices allow for underclocking. Deliberate underclocking involves limiting a processor's speed, which may affect the speed of operations, but may or may not make a device noticeably less able, depending on other hardware and desired use. Underclocking refers to alterations of the timing of a synchronous circuit in order to lower a device's energy needs. However, the proportional performance reduction is usually less than the proportional reduction in clock speed because performance is often limited by other bottlenecks: the hard disk, GPU, disk controller, Internet, network, etc. This invariably comes at the expense of some system performance. For example, a Pentium 4 processor normally clocked at 3.4 GHz can be "underclocked" to 2 GHz and can then be safely run with reduced fan speeds. This can provide increased system stability in high-heat environments, or can allow a system to run with a lower airflow (and therefore quieter) cooling fan or without one at all. Types CPU underclocking įor microprocessors, the purpose is generally to decrease the need for heat dissipation devices or decrease the electrical power consumption.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
